Learn English pronunciation to develop fluency
How to sound more like a native English speaker.
Why should you learn English pronunciation?
[Last updated on 12/07/2023]
To communicate effectively in English-speaking environments, language students need to learn English pronunciation. A good level of pronunciation not only enhances understanding, but also boosts confidence in oral communication and helps to develop English fluency.
In this blog, we look at the challenges, and provide ten practical tips to help learn English pronunciation. By incorporating these strategies into your language learning journey, you will gain the skills necessary to express yourself fluently and accurately in English.
Contents
Learn English pronunciation: The basics
- English spelling
- 26 letters (A-Z)
- 5 vowels (a, e, i, o, u)
- 26 consonant (b, c, d, f, g, etc.)
- English pronunciation
- 44 pronunciation sounds / phonemes
- 20 vowel sounds / phonemes
- 24 consonant sounds / phonemes
What are the challenges of English pronunciation?

Learning English pronunciation can be challenging for non-native speakers. This is often related English spelling, and how English pronunciation sounds and spelling differ from the first language (or mother tongue).
There are also challenges with connected speech, intonation and regional variations.
1. Individual sounds
The spelling and pronunciation of individual sounds or phonemes can be difficult for language learners for key reasons. Click on each type below for examples:
Most English pronunciation sounds have more than one spelling.
Here are some examples where one phomeme, /i:/, has different spellings.
- we
- tree
- teach
Some spellings can have more than one pronunciation sound.
Here are some examples where one spelling, “e”, has different phonemes.
- bed /e/
- she /i:/
- the /ə/
Some letters in Engish spellings are silent and not pronounced.
Here are some examples where some letters are silent in pronunciation.
- knife
- comb
Some words have extra sounds that are not in the spelling.
Here are some examples where extra sounds are not in the spelling.
- queen has a /w/ sound – qu(w)een
- uniform has a /j/ sound – (y)uniform
2. Individual words
There can also be difficulties with the spelling, pronunciation and meaning of individual words. Click on each type below for examples:
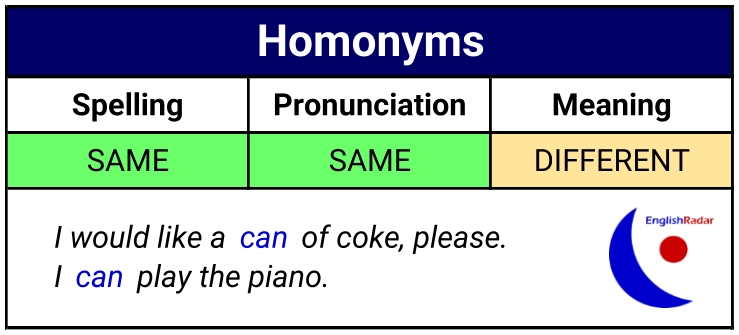
Some words are spelt the same, pronounced the same, but have different meanings (homonyms).
Examples of homonyms:
- I would like a can of coke, please. /kæn/
- I can play the piano. /kæn/
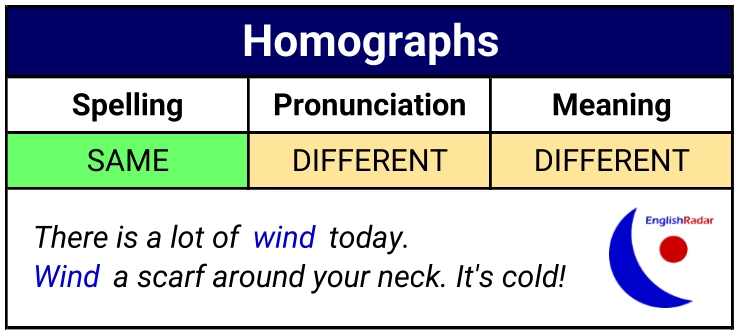
Some words are spelt the same, are pronounced differently and have different meanings (homographs).
Examples of English homographs:
- There is a lot of wind today. /wɪnd/
- Wind a scarf around your neck. It’s cold! /waɪnd/
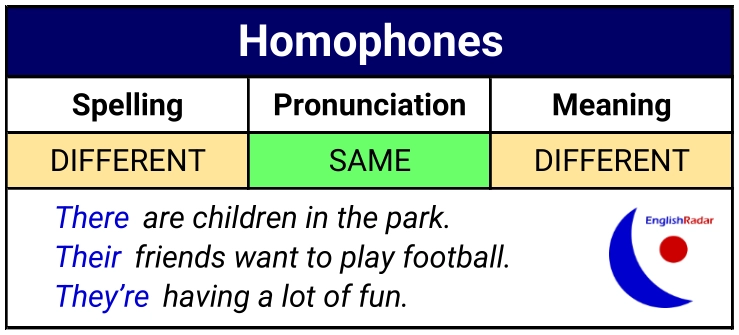
Some words are spelt differently, pronounced the same, but have different meanings (homophones).
Examples of English homophones:
- there, their, they’re
- to, two, too

3. Connected speech
English is commonly spoken with connected speech, which affects the pronunciation of connecting words. The main advantage is that connected speech makes it possible to speak faster and more smoothly. This is natural in most languages. It’s harder to have a conversation if we try to say each word separately and clearly!
With connected speech, words can sound different to when they are pronounced individually in isolation. Some words link together, and sometimes sounds are added, or sounds are left out, and sometimes sounds change! These changes can lead to difficulties in understanding natural spoken English.
Click on each type below for examples:
Catenation
When one word ends with a consonant sound and the next word starts with a vowel sound, we link words together. This is catenation. Here, the consonant at the end of the first word moves to the start of the next word.
Examples:
- “He’s in London.” is pronounced “He-sin London.”
- “Please turn off the lights.” is pronounced “Please tur-noff the lights.”
Intrusion
When one word ends with a vowel sound and the next word starts with a vowel sound, we add a new sound to connect the words together. This is intrusion. Here, we add a consonant sound to the start of the next word. The sound added is /r/, /w/, or /j/.
Examples:
- “They’re on holiday.” is pronounced “They’re ron holiday.” (with an extra /r/ sound).
- “How are you?” is pronounced “How wa you?” (with an extra /w/ sound).
- “I didn’t like the movie because the end was terrible.” is pronounced “I didn’t like the movie because the yend was terrible.”(with an extra /j/ sound).
Elision
If the first word ends with a consonant sound, and the next word starts with the same or a similar consonant sound, the sound at the start of the next word, we leave out a sound. This is elision. Here, we leave out the consonant sound at the end of the first word. This commonly involves the sounds /k/, /t/ or /d/.
Examples:
- “I walk to work.” is pronounced “I wal-to work” (without a /k/ sound).
- “She used to live in France.” is pronounced “She use to live in France” (without a /d/ sound).
Assimilation
If the first word ends with a consonant sound, and the next word starts with a consonant sound, it can be easier to change the sound that joins them together. This is assimilation. Here, we change the sound between words. This commonly involves words ending with the sounds /t/, /d/, or /n/.
Examples:
- “I get bored waiting at airports.” is pronounced “I gep-bored waiting at airports.” (where the /t/ changes to a /p/ sound).
- “He should have done better at school.” is pronounced “He should have dom better at school.” (where the /n/ changes to a /m/ sound).
- “You like to play football, don’t you?” is pronounced “You like to play football, don chu?” (where the /t/ and /j/ change to a /tʃ/ sound).
4. Word stress
When a word has more than one syllable, at least one is given more emphasis. This is known as word stress, the stressed syllable can be longer, louder, have a higher pitch and pronounced more clearly. Word stress can alter the meaning or change the way a word is understood. Here are some examples:
photograph
⚫● ●
photographer
●⚫● ●
photograpic
●●⚫●
It is also possible for one word to have two pronunication options, the first to indicate a noun, and the second to indicate a verb. For example:
present (noun)
⚫●
present (verb)
●⚫
5. Intonation
Intonation is the ‘music’ of speech! English speakers change their voice pitch and use rising and falling tones. Intonation is used to convey meaning, to emphasise words in a sentence and to express emotions. This can be challenging for langauge learners, but is an integral part of developing understanding and fluency.
6. Regional and cultural variations
English is a global language, spoken in diverse regions and countries. As a result, pronunciation can vary significantly based on regional accents and cultural influences. For learners, understanding different accents and adjusting to them can also be challenging.
Tips to learn English pronunciation and develop fluency

We have put together 10 English pronunciation tips. These are designed primarily to help your understanding of spoken English.
You can also use these tips to improve your own English pronunciation and sound more natural and fluent like a native speaker.
1. Listen to native speakers
Listening to a variety of native English speakers helps you to learn English pronunciation. You can observe how different speakers articulate sounds, stress certain syllables, and use intonation and rhythm to convey meaning. If you do this regularly, it improves your understanding of English pronunciation, develops vocabulary and improves overall listening comprehension.
Great options include listening to podcasts, watching movies or TV shows, and listening to music. We also recommend listening to news broadcasts, because the presenters usually speak more clearly than in other situations. Plus, news articles are typically shorter than other options, which means it’s easier to allocate a short time every day so that you have regular exposure to English pronunciation.
2. Learn the English pronunciation sounds
Learning pronunciation sounds or phonemes improves your listening comprehension and pronunciation skills. This involves recognising and distinguishing between the 44 different phonemes; 20 vowel sounds and 24 consonant sounds.
Some sounds are very similar which can create misunderstandings and errors in spoken English. Learning the different sounds trains you to differentiate between similar sounds (e.g., ship/sheep, hat/had) and improve your own pronunciation.
You can listen to and practise the 20 English vowel sounds and 24 English consonant sounds on our YouTube playlists.
3. Use online dictionaries
We also recommend using online dictionaries to learn English pronunciation. Dictionaries often include phonetic transcriptions to show the pronunciation sounds in individual words. Online dictionaries also include an audio example, so you can listen to and mimic the correct pronunciation.
4. Learn pronunciation and vocabulary together
When expanding your vocabulary, make pronunciation an integral part of the learning process. Pay attention to the pronunciation of new words and practice saying them aloud.
When you learn the correct pronunciation and meaning of new words together, you have a better understanding of new vocabulary and spoken English. This also helps to develop your own fluency and communication skills.

5. Record and evaluate yourself
By using a voice recorder or language learning app, you can record yourself speaking English and then listen to the playback to assess your own progress. One example is to read aloud from a book or a passage and record your voice. Then you can listen to the audiobook and compare your pronunciation to that of a native speaker.
Don’t simply focus on improving your pronunciation of individual sounds or words. You should also listen to the rhythm and intonation of whole sentences. Then you can identify areas where you need improvement and make note of them for future practice.
6. Practise tongue twisters
Reciting tongue twisters is a fun and effective tip to develop your English pronunciation skills. Tongue twisters are challenging phrases or sentences that contain repetitive sounds or difficult combinations of sounds. By repeatedly reciting tongue twisters, you can improve your clarity in pronouncing specific sounds or phonetic patterns. Additionally, tongue twisters provide a playful way to improve rhythm, fluency, and word stress.
We recommend that you start slowly to carefully form the different words and challenging sounds. Then you can gradually increase your speed as you become more comfortable to focus on rhythm and intonation. You can also record yourself and evaluate your progress at the same time.
You can find great examples of English tongue twisters and their pronunciation on the internet and YouTube.
7. Use pronunciation apps
Pronunciation apps are a valuable resource and provide a convenient and accessible way to develop pronunciation skills and gain confidence in spoken English. These apps offer interactive exercises, audio recordings, and visual guides to help learners practice and refine their pronunciation.
8. Sing English songs
Singing English songs is a fun and effective tip for English learners to develop their pronunciation skills. Songs provide a natural rhythm, melody, and intonation patterns that can greatly aid pronunciation practice. By singing along to English songs, you can develop more fluent pronunciation. This naturally includes individual sounds, stress patterns, connected speech and intonation.
Sing your heart out to practise English pronunciation in a relaxed and enjoyable manner!

9. Join langauge exchange groups
Language exchange groups bring together individuals who are interested in learning each other’s languages. This creates a mutually beneficial environment for practising pronunciation and improving spoken English. Together, you can engage in conversations with native speakers and receive immediate feedback on your pronunciation and other skills. In addition, these communities can provide an ongoing motivation to learn English and develop your fluency.
10. Take an English course with a trainer
We also recommend English lessons with qualified English trainers. An English course provides regular and structured practice to develop your English skills. Plus, a qualified trainer can adapt lessons based on your individual needs. They identify areas that you need to improve and offer continuous feedback.
We are happy to discuss our online English courses, which include one-to-one lessons with friendly and professional trainers.
What are your next steps to learn English pronunciation?
Our English pronunciation tips can support your langauge journey to develop your English fluency. With improved pronunciation, you can improve understanding and communicate effectively and confidently in English.
We also know that learning preferences are not the same for every student. Therefore, we recommend that you try some of our tips to determine what suits you best in your language journey.