What is the present continuous?
The present continuous (or present progressive) is one of the English verb tenses.
You can learn more English online by visiting our free English grammar lessons, which include other verb tenses and more grammar points.
You can also find more grammar, vocabulary and communication tasks for each English level:
Use & examples |
We use the present continuous tense to describe:

(1) Happening now (at the moment)
It describes temporary actions that started before and are still happening right now.
- I am eating dinner.
- We are running in the park.

(2) Started, but not finished
[English level A2 - English level B1]
It can also describe actions or situations that started before and are not yet finished. These are temporary and last for a limited period of time. (It might not be happening at the time of speaking.)
- She's living with her parents.
- I'm reading a great book. (but I'm not reading NOW!)

(3) State verbs
[English level A2 - English level B1]
State verbs do not usually have a continuous form, and are used in the present simple. They commonly describe something that is not an action (e.g. emotions, thoughts, relationships, senses). These verbs can be used in the continuous form when they describe an action or a process.
- He
's knowingthe best restaurants in London. - He knows the best restaurants in London.

(4) Future arrangements
This describes future events that are already planned, e.g. the time and place are already decided.
- His parents are flying to Australia on Sunday.
Form |
How do you write and pronounce the present continuous?
Form: Key points
- Use the auxiliary verb 'be' (am/is/are) + main verb (-ing).
- Contractions are commonly used with the present continuous tense.
Here are examples of the affirmative (positive) form, negative form and question form using the verb 'live'.
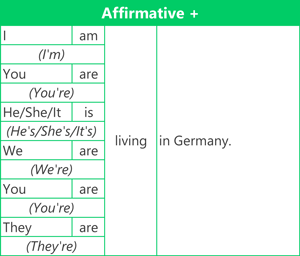
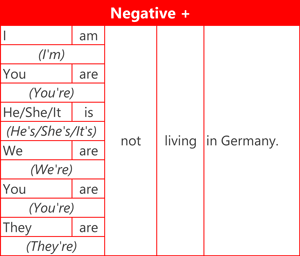
Contractions
It is also possible to contract auxiliary verb 'is + not' (aren't) and 'are + not' (isn't)
- You aren't
- He/She/It isn't
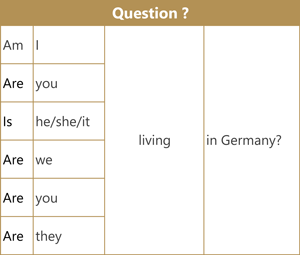
Short answers
- Yes, I am. / No, I'm not.
- Yes, you are. / No, you're not.
Pronunciation
We commonly use contractions (e.g. 'I'm meeting friends' or 'He isn't working today') for the present continuous tense, especially when speaking English.
Notes |
Spelling exceptions for verbs
Sometimes we need to remove a letter, and other times we need to add another letter. Here are the exceptions:
1) One 'e' at the end of a verb
Remove the final 'e' and add 'ing'.
Examples:
[live] I'm living in Germany.
[save] I am saving money for a new car.
* Verbs ending in 'ee'
These follow the normal rules.
Examples:
[see] He's seeing his friends.
2) Verb ends with consonant + one stressed vowel + one consonant
Double the final consonant and add 'ing'.
Examples:
[stop] I'm stopping the car.
[swim] We're swimming in the sea.
* Verbs ending with an unstressed vowel
These follow the normal rules, and the last consonant is not doubled.
Examples:
[develop] They're developing a new idea at the company.
3) Verb ends in 'l' (British English)
Double the final consonant and add 'ing'.
Examples:
[travel] I'm travelling with friends.
4) Verb ends with 'ie'
Change 'ie' to 'y' and add 'ing'
Examples:
[lie] She's lying to the teacher.
5) Verb ends with 'ic'
Add 'k' before 'ing'.
Examples:
[panic] He's panicking about the exam.
Quizzes |
Quiz 1: Things happening at the moment
What are the family doing at home now?
[Topic: Free time]
Type the verbs in the present continuous tense and use the affirmative, negative or question form.