What is the past continuous?
The past continuous (or past progressive) is one of the English verb tenses.
You can learn more English online by visiting our free English grammar lessons, which include other verb tenses and more grammar points.
You can also find more grammar, vocabulary and communication tasks for each English level:
Use & examples |
We use the past continuous tense to describe:

(1) Temporary actions in the past
[English level A2 - English level B1]
It describes a temporary action that was taking place over a period of time in the past. The action does not continue to the present. It can also show two actions happening at the same time in the past.
- I was watching television yesterday evening.
- I was talking on the phone while my mum was cooking dinner.

(2) Gives background information around a specific time in the past
[English level A2 - English level B1]
When one past action happened in the middle of another past action, we can use the past continuous and past simple together.
⟩ The past continuous is used for temporary actions or situations that were already happening.
⟩ The past simple describes something that happens in the middle of (or interrupts) the longer background action.
- She was driving the car when the phone rang.

(3) Repeated actions
The past continuous can also emphasise repeated actions in the past, and often with expressions like 'always', 'continually', 'forever'.
- She was always complaining about the weather.
- They were continually borrowing money from his parents.
Form |
How do you write and pronounce the present continuous?
Form: Key points
- Use the auxiliary verb 'be' (was/were) + main verb (-ing).
- Contractions are commonly used with the negative past continuous tense.
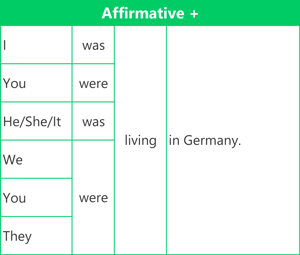
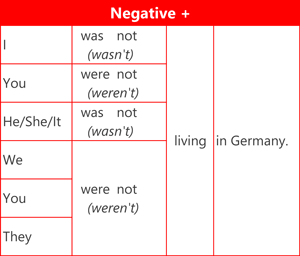
Here are examples of the affirmative (positive) form, negative form and question form using the verb 'live'.
Contractions
We don't use contractions between the subject and the auxiliary verb in the affirmative. For example, 'You were' cannot be contracted for the past continuous. (This is only possible with the present continuous.)
Contractions
Contractions can only be used in the negative form between the auxiliary verb and 'not'.
- was not = wasn't
- were not = weren't
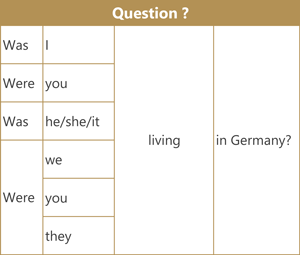
Short answers
- Yes, I was. / No, I wasn't.
- Yes, you were. / No, you weren't.
Pronunciation
We commonly use contractions for the negative past continuous tense (e.g. 'I wasn't meeting friends' or 'He wasn't working'), especially when speaking English.
Notes |
Spelling exceptions for verbs
Sometimes we need to remove a letter, and other times we need to add another letter. Here are the exceptions:
1) One 'e' at the end of a verb
Remove the final 'e' and add 'ing'.
Examples:
[live] I was living in Germany.
[save] I was saving money for a new car.
* Verbs ending in 'ee'
These follow the normal rules.
Examples:
[see] He was seeing his friends.
2) Verb ends with consonant + one stressed vowel + one consonant
Double the final consonant and add 'ing'.
Examples:
[stop] I was stopping the car.
[swim] We were swimming in the sea.
* Verbs ending with an unstressed vowel
These follow the normal rules, and the last consonant is not doubled.
Examples:
[develop] They were developing a new idea at the company.
3) Verb ends in 'l' (British English)
Double the final consonant and add 'ing'.
Examples:
[travel] I was travelling with friends.
4) Verb ends with 'ie'
Change 'ie' to 'y' and add 'ing'.
Examples:
[lie] She was lying to the teacher.
5) Verb ends with 'ic'
Add 'k' before 'ing'.
Examples:
[panic] He was panicking about the exam.
Quizzes |
Quiz 1: Giving background information around a specific time in the past
What was happening when the football started?
[Topic: Free time]
Type the verbs in the past continuous tense and use the affirmative, negative or question form.