What is the past perfect simple?
The past perfect simple is one of the English verb tenses.
You can learn more English online by visiting our free English grammar lessons, which include other verb tenses and more grammar points.
You can also find more grammar, vocabulary and communication tasks for each English level:
Use & examples |
The past perfect simple tense refers to 'the past in the past' and we use it to describe:

(1) Past before the past
It describes actions or situations that happened/finished before another time in the past. It is commonly used with the past simple.
- I'd (already) cooked (1) when my wife arrived (2) back from work.
- I hadn't cooked (yet) (1) when my wife arrived (2) back from work.
Form |
How do you write and pronounce the past perfect simple?
Form: Key points
- Use the auxiliary verb 'had' + main verb (Past participle).
- To form the past participle of main verbs, add 'ed' to the base form of the verb, which is the infinitive without 'to'.
Here are examples of the affirmative (positive) form, negative form and question form using the verb 'live'.
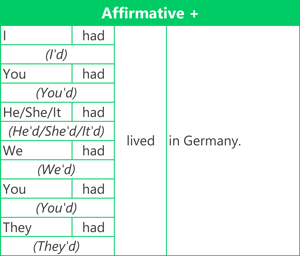
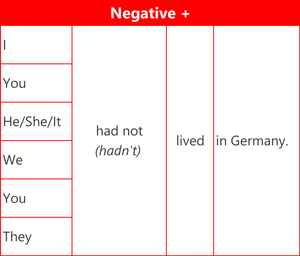
Contractions
It is also possible to contract subject pronouns with auxiliary verb + 'not'
- I'd not
- He'd/She'd/It'd not
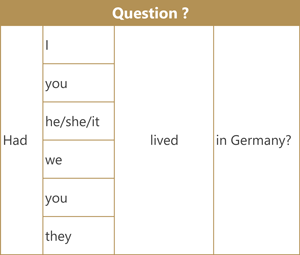
Short answers
- Yes, I had. / No, I hadn't.
- Yes, you had. / No, you hadn't.
Pronunciation
We commonly use contractions (e.g. 'I hadn't met friends' or 'He hadn't worked') for the past perfect simple tense, especially when speaking English.
The past perfect simple with 'ed' has three different pronunciation sounds.
- /t/ (e.g. worked, helped) - when 'ed' comes after an unvoiced consonant sound.
- /d/ (e.g. stayed, lived) - when 'ed' comes after a voiced consonant or a vowel sound.
- /ɪd/ (e.g. started, decided) - when 'ed' comes after the sounds /t/ and /d/.
Notes |
For the past perfect simple, we have extra information about:
- spelling exceptions for verbs and
- time expressions that you can use.
Spelling exceptions for verbs
The past participle for regular verbs is the same as the past tense form and ends with 'ed'.
Sometimes we need to remove a letter, and other times we need to add another letter. Here are the exceptions:
1) One 'e' at the end of a verb
Add 'd' at the end of the base form.
Examples:
[live] I'd lived in Germany.
[save] I hadn't saved money for a new car.
2) Verb ends with consonant + one stressed vowel + one consonant
Double the final consonant before -ed'.
Examples:
[stop] I'd stopped the car.
* Verbs ending with an unstressed vowel
These follow the normal rules, and the last consonant is not doubled.
Examples:
[develop] They'd developed a new idea at the company.
3) Verb ends in 'l' (British English)
Double the final consonant before -ed'.
Examples:
[travel] I'd travelled with friends.
4) Verb ends with 'ic'
Add 'k' before -ed'.
Examples:
[panic] He'd panicked about the exam.
5) Irregular verbs
There are many irregular verbs which don't follow the rules and you just need to remember them!
Examples:
[see] He'd seen this film.
Time expressions used with past perfect simple
Time markers can be used with the past perfect simple and connect (or relate to) two different times in the past.
1) for
This connects a period of time in the past to a later time in the past.
Examples:
I'd already worked at this company for two years (when I got promoted).
2) by / by the time / when
This is used when something happened before (not later than) a specific time in the past.
Examples:
By 4 o'clock, he'd finished all his emails.
By the time he left work, he'd finished all his emails.
I'd already worked at this company for two years, when I got promoted.
3) just
This shows that something finished a short time before a later action in the past.
Examples:
We'd just eaten lunch.
4) already
This shows that something was finished earlier than expected.
Examples:
She'd already gone home.
5) yet
This is used for negatives and questions about situations that were expected to happen.
Examples:
My wife arrived home at 6 0'clock, and I hadn't cooked dinner yet.
6) before / after
These expressions can be used emphasis the sequence of events. It is not necessary to use the past perfect when the sequence of events is clear.
Examples:
The film had started before I ate dinner. = The film started before I ate dinner.
The film started after I'd eaten dinner. = The film started after I ate dinner.
Quizzes |
Quiz 1: Things that happened before another time in the past
[Topic: Family]
Type the verbs in the past perfect simple tense and use the affirmative, negative or question form.